Host a Decentralized Private Proxy Server
This article is short and sweet - it shows how you can use Diode to host a decentralized private proxy server.
Here is a 32s video demonstrating how to set this up.
This can have the following benefits:
- No static IP address required - host your proxy on a home or office network, or anywhere you don’t have, or don’t want to expose, a static IP address
- No proxy connection meta information leaked - proxy connections are tunneled via the Diode network
- No IP address leaked - proxy clients do not connect directly to your Proxy IP, reducing the likelihood your proxy will get blocked
- Easy to do - the Diode CLI has a built-in proxy server and handles all the tunneling with a simple command
This article assumes you are using Linux, but it will pretty much work the same way for all supported OSes.
#Proxy Server Instructions
- Download and install the Diode CLI from https://diode.io/download
- Run the Diode CLI as a proxy exit node by invoking it from a terminal as:
diode publish -public 1080:1080 -socksd
This will print out something like:
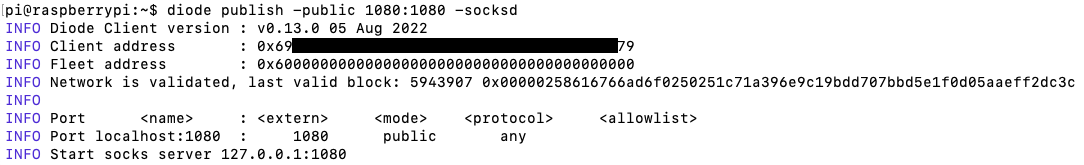
The “Client Address” is your proxy server’s decentralized address - you will need to direct all the proxy client connections to that address. Let’s pretend this example’s Client Address is 0x6900000000000000000000079
- Make it persistent on your system by adding the Diode command to systemd (assuming Linux)
- You can follow the instructions here
- Modify the ExecStart line to
ExecStart=/home/pi/opt/diode/diode publish -public 1080:1080 -socksd - Some people find it handy to force-restart the service every day by adding the line
RuntimeMaxSec=86400
#Proxy Client Instructions
- Download and install the Diode CLI from https://diode.io/download
- Run the Diode CLI as a proxy client by binding its localhost port 1080 to your proxy server’s Client Address from a terminal as:
diode -bind 1080:0x6900000000000000000000079:1080
Now you have a secure proxy connection from your client device to your proxy server!
-
Use it by setting up your system, a browser, or other application to connect to a Socks5 proxy on localhost:1080